
Presenting Bespoken
The Seamless AI Stylist Web Plug-In for an Unparalleled Style Advisory Experience Tailored to Your End Consumers
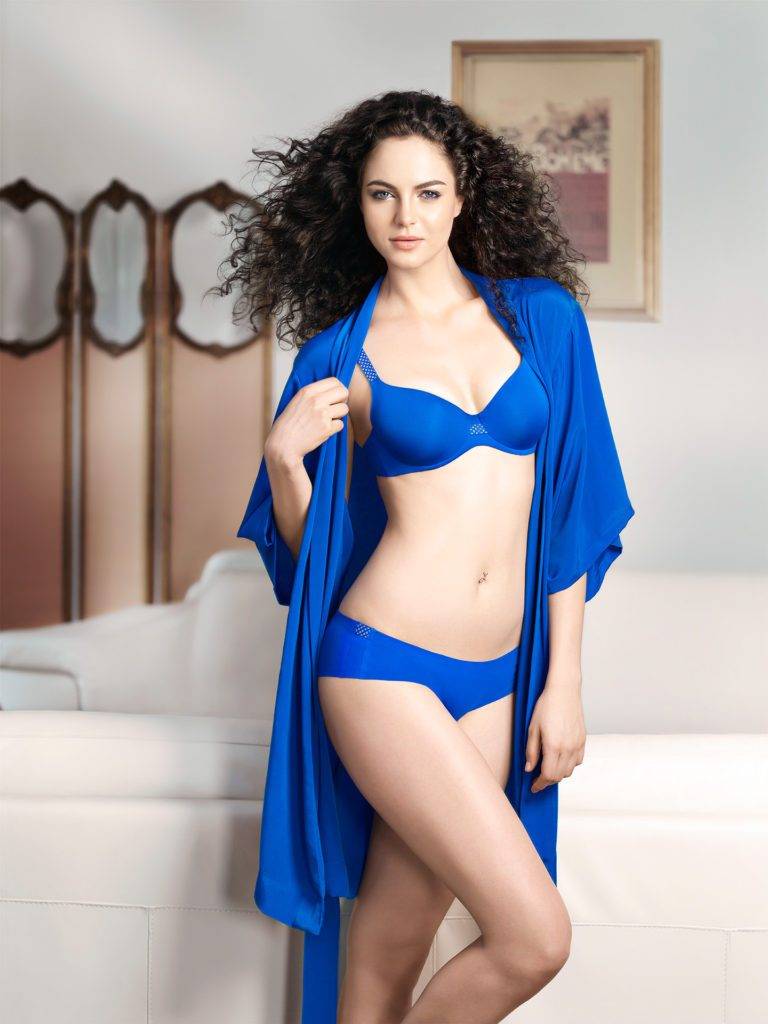
👗 Personalised Style assistance for every body shape👗
Discover the power of Alina, our AI Stylist, in providing tailored fashion advice for all body shapes. Alina understands the five universal body shapes – Pear, Hourglass, Apple, Rectangle, and Inverted Triangle. With Alina’s guidance, your end consumers can effortlessly choose outfits that enhance their unique features while staying true to your brand’s collection and style DNA. It’s personalized styling made easy.
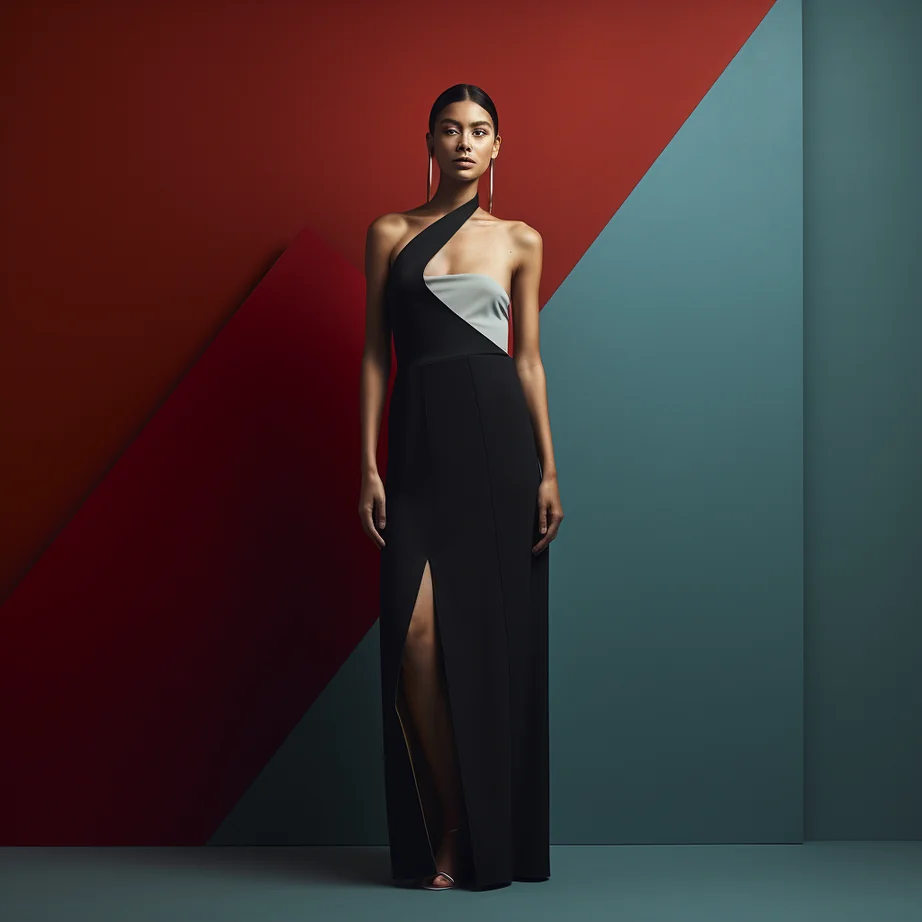
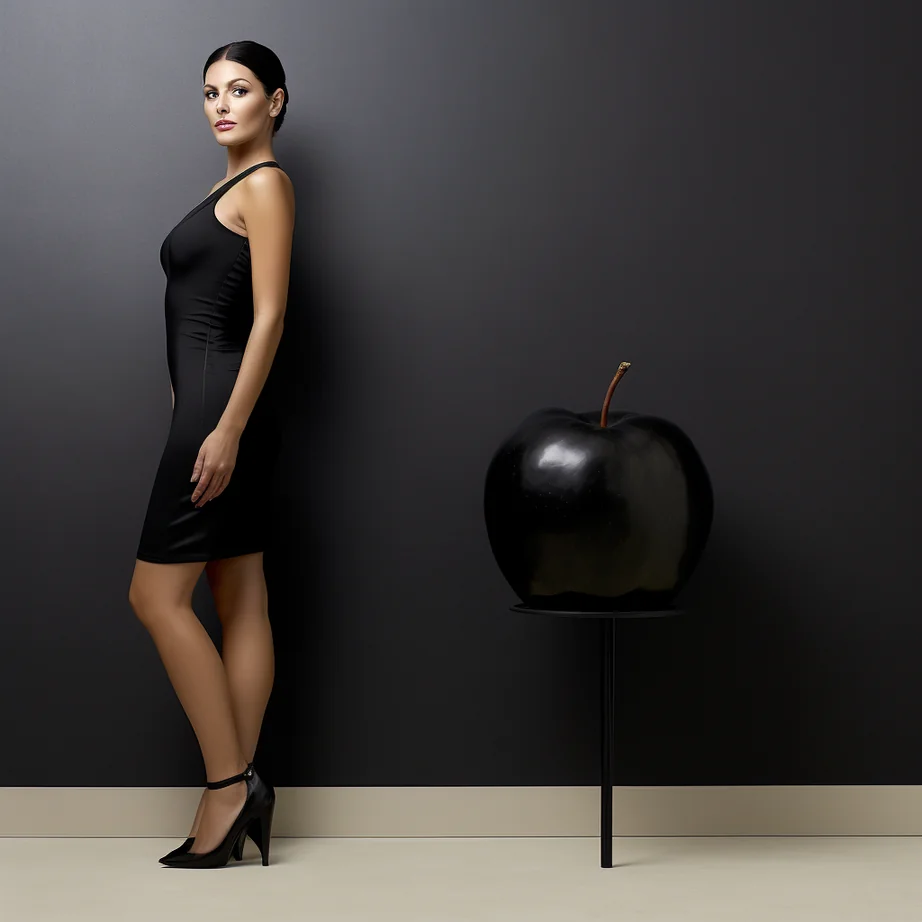
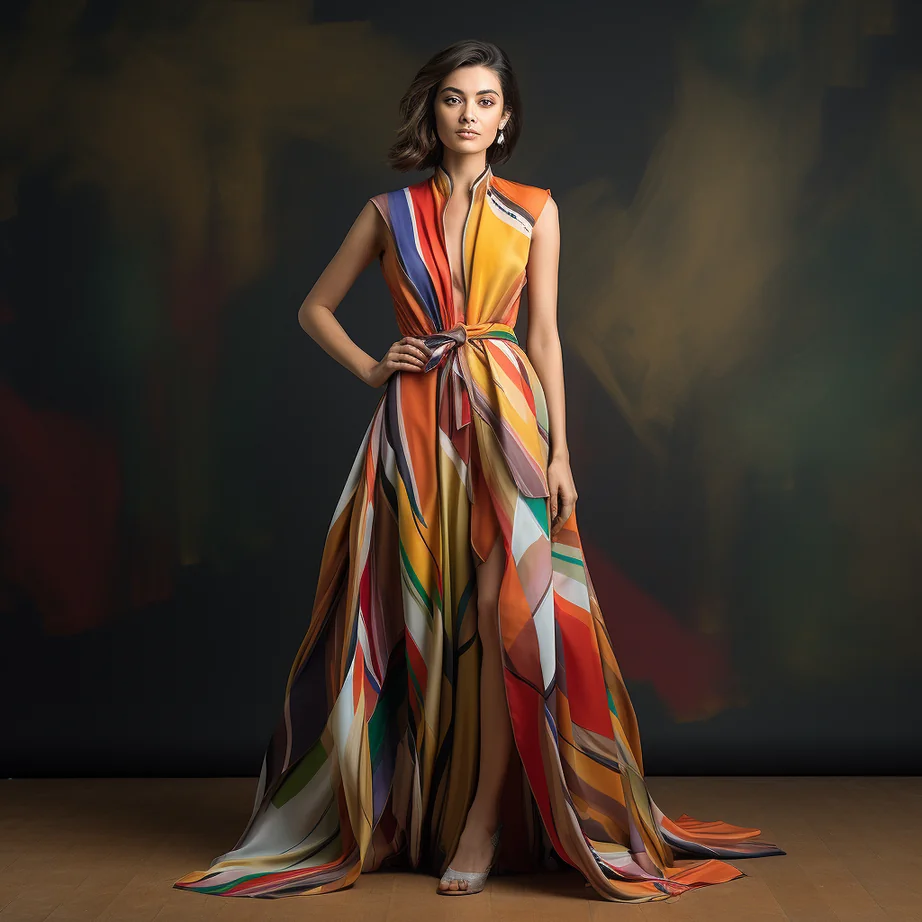
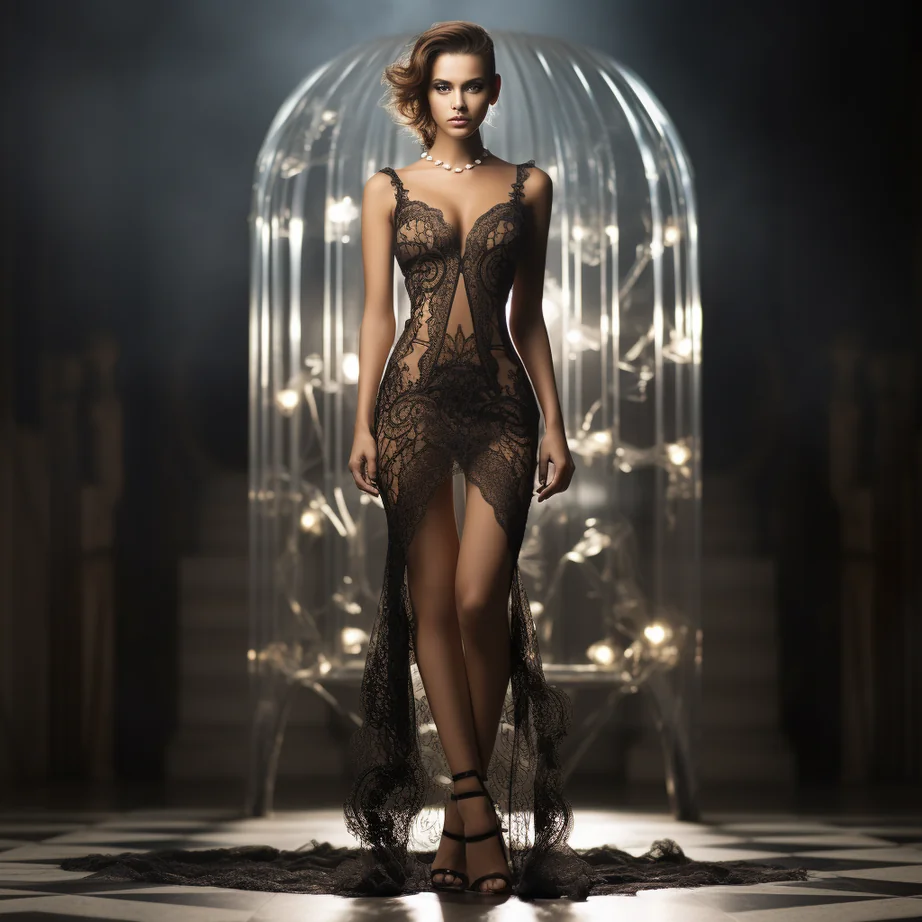




👗 Discover Alina, Your AI Stylist Companion! 👗
Click the “Know More” button to offer your brand’s end consumers personalized style recommendations that perfectly harmonize with your collection and style DNA. Let Alina, our AI stylist, curate distinctive and personalized suggestions that align with your end consumers’ preferences, while mirroring your brand’s essence.
W
wonderment
Wonderment is the heartbeat of Design Wolf Studio, where entrepreneurial designers find the ideal breeding ground for innovation. This dynamic platform fuels the creative spirit of design entrepreneurs, providing them with the tools and environment to ideate, conceptualize, and craft new products that resonate with their vision. From ideation to realization,
O
optmise
At Design Wolf Studio, design entrepreneurs harness the power of technology to conquer intricate design challenges. Our tailored design process, guided by innovation, refines creations to perfection. Teaming up with Tukatech, we revolutionize manufacturing. Their algorithm, an epitome of fabric-saving expertise, enhances production efficiency and sustainability.
L
leverage
At Design Wolf Studio, we excel in leveraging innovation to give design entrepreneurs a distinctive edge from the very inception of their ideas. Through our strategic partnership with Design Wolf's Tuka Center, entrepreneurs harness a suite of cutting-edge services including digital pattern making, grading, marker making, and 3D visualizations, all seamlessly integrated to offer unmatched leverage.
F
fulfill
Our Bespoken SAAS plugin empowers brands and retailers to meet an essential consumer need - a personalized fit that enhances their confidence and style. This strategic advantage ensures a flattering look, fulfilling the core aspiration of fashion.By integrating advanced technology, we ensure that each individual's unique style is complemented by a flawless fit,

Design Wolf serves as the Swiss Knife for the Fashion World, embodying the acronym WOLF: Wonderment, Optimization, Leverage, and Fulfillment, driving innovation across the realm of fashion.
Transform Your Fashion Vision: Elevate Your Brand with Expert Product Development Solutions
Optimized Enhancement for Faster, Better, and Cheaper Design Processes
Leverage fashion to your advantage
Fulfillment is when your Product transforms into an Experience
Welcome to a Fashion Revolution
At Design Wolf Studio, we believe fashion should be an expression of your true self. That's why we're thrilled to present Bespoken, our revolutionary AI-powered platform that brings the magic of personalized fashion experiences to your fingertips.
Your Style, Amplified
With Bespoken, your customers will embark on a transformative fashion journey like no other. Our advanced AI recommendation engine analyzes their unique preferences, body shapes, and occasion needs to curate tailored collections that speak directly to their style aspirations.
Why Choose Bespoken?
Unleash Creativity: Empower your customers to explore their style boundaries. Bespoken's personalized recommendations ignite their imagination and open doors to new fashion horizons, helping them create extraordinary style statements. Boost Engagement:
Captivate your audience with a seamless and immersive shopping experience. Bespoken's AI-driven solutions enhance customer satisfaction, increase time spent on your platform, and drive higher conversion rates.
Stay Ahead of Trends: Gain a competitive edge by harnessing the power of data. Bespoken's deep insights into emerging trends, customer preferences, and market demands equip you with the knowledge to lead the fashion industry.
Introducing The 7 Practices: Unlocking Innovation in Fashion
Trend forecasting, design development, prototyping, and fashion samples
At Design Wolf Studio, we believe that innovation is the key to transforming the fashion industry. That's why we're excited to offer you our exclusive ebook, "The 7 Practices: Unlocking Innovation in Fashion." Discover the game-changing strategies and insights that can propel your brand to new heights of success.
Why The 7 Practices?
Inspire Creativity: Gain a fresh perspective on innovation in fashion. Explore real-world examples and case studies that will ignite your creativity and empower you to think outside the box.
Stay Ahead of the Curve: Unlock the secrets behind industry disruptors and pioneers who have redefined the fashion landscape. Learn how to anticipate trends, embrace emerging technologies, and stay ahead of the competition.
Drive Business Growth: Innovate your way to success. Discover proven strategies that can elevate your brand, engage your customers, and drive business growth in today's dynamic fashion market.
What Our Clients Say About Design Wolf Studio?
Bespoken is first of its kind Phygital Platform where we get to collaborate with the design community. Bespoken helps us to reach the right consumers profile. It's cool feature is the Preview Event where I get to test my new ideas, concepts and collections. It helps me get consumer insights before I decide my launch strategy.

Disha Nath Sepoy
Founder at YūGEN
I am thrilled with the service I received from Bespoken, which was unparalleled. What I really loved about them was the ease of use of the sleek interface and the convenience of the platform. I really appreciate the personal touch by the proprietors and making us comfortable even sitting far far away in other country . The designers they are letting us shop from have amazing quality and impeccable taste

Dimple Chhibber
Fashionista
This platform has been by all means a great space to collaborate with the design community. We could create, curate and collaborate our new collection "here and now" of earth songs seamlessly and did a preview session with our clients to gain head strat. Our 360 degree wardrobe session with client was an ultimate experience to understand what our consumers really wants. Bespoken team has been helpful in so many ways..

Anuja Goel
Founder Earth Songs
Bespoken as a platform is a very good tool for budding artists, fashion designers and curators of all kinds. It helps and supports you at all stages of creation, be it event planning, customer acquisition and new collection launches. It's subscription model is amazingly reasonable and can be used very effectively.

Anju (Singhal) Shetty
Founder at Art'eque
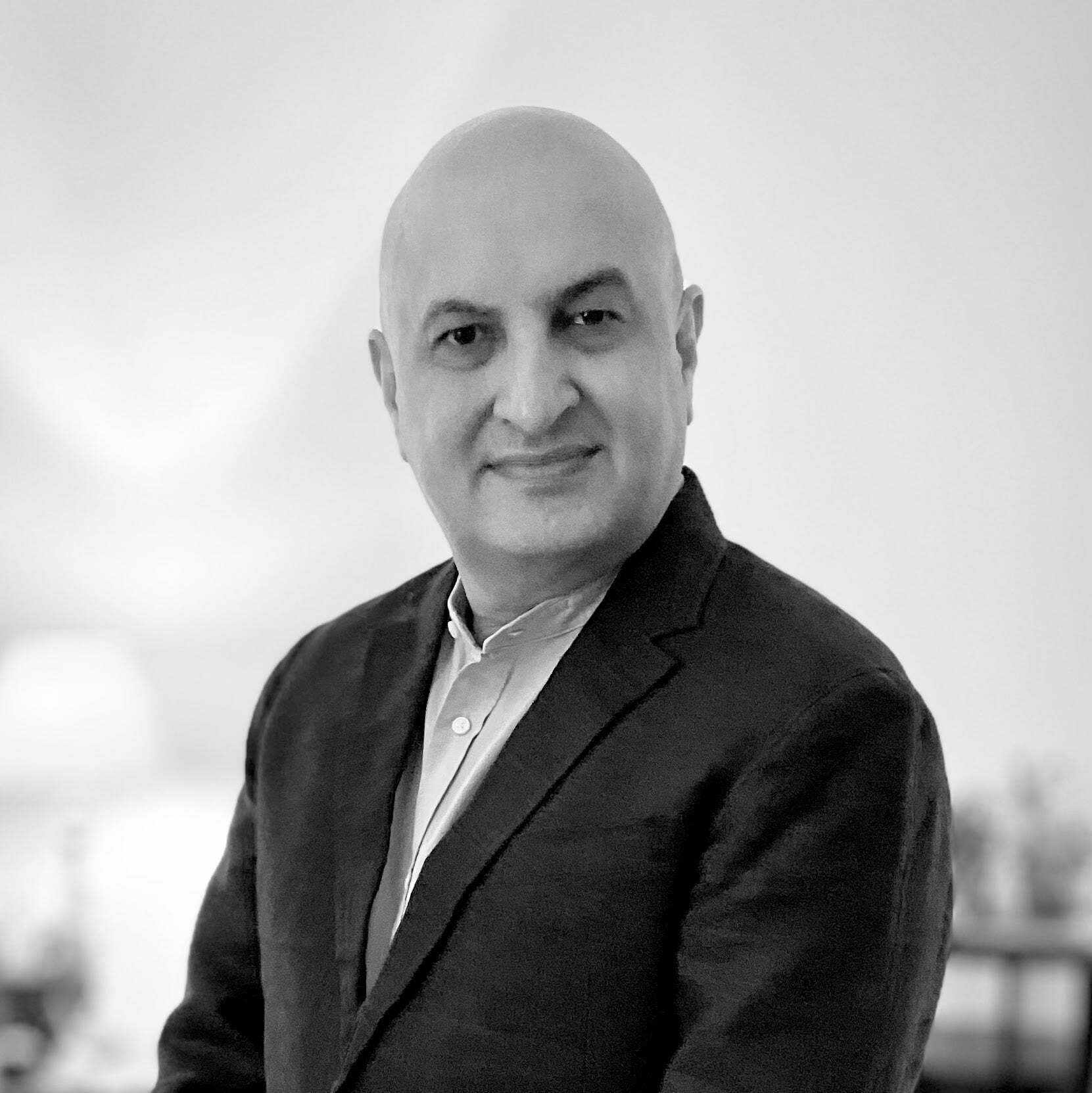
Founders Fashion Journey
In the bustling heart of Mumbai, Jagdish's odyssey began at Raymond Limited. As Manager - Retail, his days were colored by the unique tapestry of Indian retail. In the echoing hum of fabric looms and amidst aisles lined with the latest trends, he sculpted a vision for global fashion fusion.
Shoppers Stop beckoned next. Here, Jagdish refined his expertise, ensuring every garment was not just an article of clothing but a narrative. Each collection, a testament to his understanding of consumer desires and the pulse of Mumbai's dynamic fashion scene.
The balmy Indonesian archipelago was his next canvas. Starting at PT. Texmaco and RIMO and culminating as VP of Sourcing and Merchandising at Matahari, Jakarta became a pivotal chapter. Here, he married the heart of Indian retail with Southeast Asian vibrancy. Orchestrating sourcing ventures from China, he bridged the East and West, crafting a harmonious blend of diverse cultures and fashion sensibilities.
Upon Jagdish's return to India, Bengaluru's vibrant mix of tech innovation and deep-rooted fashion traditions greeted him. As he navigated roles at Lifestyle International and Reliance Retail, he melded global trends with India's unique style palette. However, the real game-changer came with Flipkart. Steering its private label and licensing endeavors, Jagdish birthed unique brand collections, with the standout being the exclusive Ducati fashion line. This era was a dance of traditional retail with the pulsating beats of India's booming digital marketplace.
Sri Lanka's sun-kissed shores witnessed Jagdish's rendezvous with technology. As Aviraté's CEO, he forged ties with European and US designers, championing innovations in fit through TukaTech. From the bustling markets of Germany and the Middle East to the snowy terrains of Canada, his reach extended, weaving a global tapestry. His foray into lingerie further showcased his versatility, revealing a maestro at work.
Design Wolf Studio in Bengaluru is Jagdish's magnum opus. It's where his decades-long voyage across global fashion vistas converge. More than just a studio, it's a culmination of experiences spanning continents. Trend forecasting, digital solutions, brand development—it's where the world of fashion finds a home.
This odyssey, led by Jagdish Chawla, narrates a tale not just of fashion’s evolving landscape but of a visionary who danced to the tunes of global threads, weaving a legacy unlike any other.
Gallery




Services
Fashion Design and Development:
Collaborative design bringing your visions to life.
Efficient pattern making, prototyping, and sample development.
Streamlined production processes for quicker turnarounds.
Digital Pattern Creation:
Tuka Center's advanced CAD technology for precise patterns.Cost-effective grading and marker making.
Sample Development:
Craft compelling prototypes that reflect your design vision. Precision in translating ideas into tangible samples. Pattern Optimization:
Pattern Optimization:
Efficient pattern nesting and marker making.Minimized material wastage and production costs.
Digital Prototyping and Visualization:
Realistic 3D previews for faster decisions.Reduced need for physical samples.
Design Consultation:
Expert advice on design strategies and market opportunities.Enhancing your brand identity.






 This odyssey, led by Jagdish Chawla, narrates a tale not just of fashion’s evolving landscape but of a visionary who danced to the tunes of global threads, weaving a legacy unlike any other.
This odyssey, led by Jagdish Chawla, narrates a tale not just of fashion’s evolving landscape but of a visionary who danced to the tunes of global threads, weaving a legacy unlike any other.